2021. 7. 24. 16:57ㆍ그래픽스/opengl
1. Shaders
= GPU에서 동작하는 프로그램 (little programs tat rest on the GPU)
= 파이프라인 각 단계마다 사용되는 shader가 다름
= shader는 입력값을 출력값으로 변환시키는 프로그램으로 아주 독립적인(isolated) 프로그램
= 서로 통신할 수 없음. 유일한 comunication은 입력값과 출력값을 통해서하는것
2. GLSL
= Shader는 C언어와 비슷한 GLSL로 작성한다.
= GLSL is tailored for use with graphics and contains useful features : vector + matrix manipulation.
= 항상 버전 선언으로 시작
= 그다음으로 입력 변수와 출력변수들이 나오게됨
= uniform이 나오고, 그 후엔 main 함수
= shader의 시작지점은 main 함수부터 -> 모든 입력 변수를 처리, 출력 변수로 결과를 출력
#version version_number
in type in_variable_name;
in type in_variable_name;
out type out_variable_name;
uniform type uniform_name;
void main()
{
// 입력 값을 처리하고 그래픽 작업을 합니다.
...
// 처리된 것을 출력 변수로 출력합니다.
out_variable_name = weird_stuff_we_processed;
}
Vertex shader
= 각각의 입력변수 : vertex attribute
= 하드웨어에 의해 제한되어 선언할 수 있는 최대 개수가 정해짐
=> 4-component vertex attribute를 최소 16개까지 보장 (대부분 작업에서 충분)
=> GL_MAX_VERTEX_ATTRIBS 를 통해 하드웨어의 허용 개수를 알 수 있다.
int nrAttributes;
glGetIntegerv(GL_MAX_VERTEX_ATTRIBS, &nrAttributes);
std::cout << "Maximum nr of vertex attributes supported: " << nrAttributes << std::endl;
GLSL Types
= c언어와 같은 언어에서 볼 수 있는 기본적인 타입들의 대부분을 가지고 있다. (int, float, double, uint, bool)
= 두가지 컨테이너 타입 vector, matrics
GLSL Vectors
= Vector 는 1~4가지 요소를 가진 컨테이너
= n은 components의 개수
- vecn: n개의 float 타입
- bvecn: n개의 boolean 타입
- ivecn: n개의 integer 타입
- uvecn: n개의 unsigned integer 타입
- dvecn: n개의 double 타입
= float 타입이 대부분 충분하기 때문에 vecn을 보통 사용
= component 접근 : vec.x .y .z .w
= rgba : 컬러값
= stpq : 텍스쳐 좌표
GLSL Vector swizzling
vec2 someVec;
vec4 differentVec = someVec.xyxx;
vec3 anotherVec = differentVec.zyw;
vec4 otherVec = someVec.xxxx + anotherVec.yxzy;= 새로운 벡터를 성성하기위해, component의 조합을 표시
vec2 vect = vec2(0.5, 0.7);
vec4 result = vec4(vect, 0.0, 0.0);
vec4 otherResult = vec4(result.xyz, 1.0);= 모든 유형의 입출력에 사용할 수 있는 유연한 데이터 타입
Ins and Outs
= 입력과 출력 : 키워드 in, out 로 정의
= 각 shader는 이 키워드들로 출력 변수가 다음 shader의 어떤 입력 변수와 맞는지 지정할 수 있음
= vertex shader : 일정한 형태의 입력을 받아야함.
= = == vertex 데이터를 곧바로 입력으로 받음.
= = = = 어떻게 구성되어있는지 정의 = location 메타데이터와 함께 입력변수지정
= = = = CPU에 vertex attribute를 구성할 수 있음
= = = = layout (location = 0) => 입력에 대해 별도의 layout 명시, vertex 데이터와 연결
= = = = glGetAttribLocation 함수를 사용하여 연결할 수 있으나 shader에 설정하는것이 권장됨
= fragment shader : 최종 출력 컬러를 생성해야함
= = = = vec4 타입의 컬러 출력 변수가 필요
= = = = fragment shader에서 출력 컬러 지정하는 것이 실패되면 검정 or white 로 렌더링됨
shader 간 통신
= 데이터를 shader 에서 shader로 넘기고싶으면, 보내는 shader에서 출력을 선언해야하고
= 받는쪽에서도 출력을 선언해야함.
= 양쪽의 타입과 이름이 같으면 OpenGL은 그 변수들을 연결 시켜 shader 간에 데이터를 보낼 수 있음
(program 객체의 연결이 완료되면)
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos; // the position variable has attribute position 0
out vec4 vertexColor; // specify a color output to the fragment shader
void main()
{
gl_Position = vec4(aPos, 1.0); // see how we directly give a vec3 to vec4's constructor
vertexColor = vec4(0.5, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // set the output variable to a dark-red color
}#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec4 vertexColor; // the input variable from the vertex shader (same name and same type)
void main()
{
FragColor = vertexColor;
}= vertex shader 에 vec4 타입 선언 => 출력 , fragment shader => 입력 선언 => 통신완료!
Uniforms 설정
= CPU위의 응용 프로그램에서 GPU 위의 shader 로 데이터를 전달하는 vertex attribute와는 다른 방법.
= uniform 은 전역변수로, shader 프로그램 객체에서 고유한 변수ㅀ
= 모든 파이프라인의 단계에서 모든 쉐이더가 접근할 수 있는것
= uniform 은 값을 reset 하거나 updated 하기 전까지 유지한다.
= 타입과 이름 앞에 uniform 키워드를 추가해야함.
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
uniform vec4 ourColor; // we set this variable in the OpenGL code.
void main()
{
FragColor = ourColor;
}= 전역 변수이기 때문에 fragment shader에서 다시 vertex 로 갈 필요가 없음
= Vertex shader 에서 uniform을 사용하지 않으므로, 정의할 필요 없음
| GLSL shader 코드에서 사용하지 않는 uniform 변수를 선언하면, 컴파일된 버전에서 자동으로 그 변수를 삭제하여 오류가 생길 수 가 있다. |
= 현재 uniform 변수인 ourColor는 비어있음,
float timeValue = glfwGetTime();
float greenValue = (sin(timeValue) / 2.0f) + 0.5f;
int vertexColorLocation = glGetUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "ourColor");
glUseProgram(shaderProgram);
glUniform4f(vertexColorLocation, 0.0f, greenValue, 0.0f, 1.0f);= 데이터 삽입방법
= = = = 1) shader 에서 uniform attribute의 index/ location을 찾아야함.
= = = = 2) uniform의 index/ location을 알아내기만 하면, 값을 수정할 수 있음.
= 시간에 따라 색 변경
= = = = 1) glfwGetTime => 초단위로 실행시간 검색 (timer measures time elapsed since the call to glfwInit)
= = = = 2) sin 함수로 0.0 - 1.0 사이의 값으로 변환
= glGetUniformLocation 함수가 -1 리턴 : location을 찾지 못한것.
= glUniform4f 함수를 사용하여 uniform 변수의 값을 설정할 수 있음.
= Uniform 값을 수정할때 현재 활성화된 shader program의 값을 변경하는거니 glUseProgram을 호출해서 활성화
오버로딩을 지원하지 않음 => core : C라이브러리 => 접미사
|
Uniforms 사용
= 렌더링 루프안에서 uniform을 수정을 해줘야함.
while(!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
// input
processInput(window);
// render
// clear the colorbuffer
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// be sure to activate the shader
glUseProgram(shaderProgram);
// update the uniform color
float timeValue = glfwGetTime();
float greenValue = sin(timeValue) / 2.0f + 0.5f;
int vertexColorLocation = glGetUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "ourColor");
glUniform4f(vertexColorLocation, 0.0f, greenValue, 0.0f, 1.0f);
// now render the triangle
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
// swap buffers and poll IO events
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
3. More Attributes
컬러 데이터 추가
float vertices[] = {
// positions // colors
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // bottom right
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // bottom left
0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f // top
};= vertex shader에 보낼 추가 데이터가 있기 때문에
= vertex attribute 입력으로 컬러값도 받도록 vertex shader 수정
= layout (location = 1) 로 컬러값을 받음
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos; // the position variable has attribute position 0
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aColor; // the color variable has attribute position 1
out vec3 ourColor; // output a color to the fragment shader
void main()
{
gl_Position = vec4(aPos, 1.0);
ourColor = aColor; // set ourColor to the input color we got from the vertex data
}= fragment의 컬러를 위해 uniform을 사용할 필요가 없으니 in 키워드 사용
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec3 ourColor;
void main()
{
FragColor = vec4(ourColor, 1.0);
}
vertex attribute pointer
= 추가적인 vertex attribute를 추가하고,
= VBO의 메모리를 수정하였기 때문에
= vertex attribute pointer를 다시 구성해야함.

= VBO 메모리의 수정된 데이터는 위와 같음.
= 현재 layout을 알고 있으면 glVertexAttribPointer 함수를 사용하여 vertex 형식을 수정할 수 있다.
// position attribute
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// color attribute
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(float), (void*)(3* sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);= stride 값을 다시설정해야고, 컬러에서 offset 지정
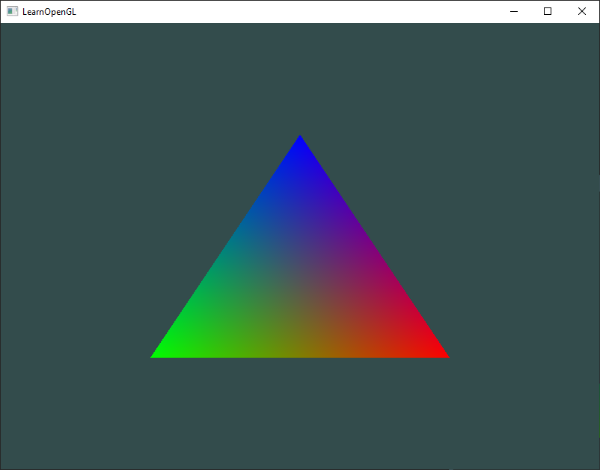
=> fragment interpolation 으로 인해 색이 퍼짐
=> 삼각형을 렌더링할때 rasterization 단계는 더 많은 fragment를 생성
=> 삼각형의 어느 부분을 맡고 있는지에 기반하여, 각 fragment를 생성
=> 그다음 fragment의 위치를 결정
=> 이 위치들을 기반으로, fragment shader의 모든 입력 변수를 보간 (interpolate)함.
=> fragment interpolation은 fragment shader의 모든 입력 attribute에 적용됨.
4. shader class
= 소스코드로 관리, 디스크에서 shader를 읽고, 컴파일, 연결, 오류확인하는 class를 만들면 편리하다.= 이식성을 위해 헤더파일에 전체적으로 클래스 생성.
#ifndef SHADER_H
#define SHADER_H
#include <glad/glad.h> // include glad to get all the required OpenGL headers
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
class Shader
{
public:
// the program ID
unsigned int ID;
// constructor reads and builds the shader
Shader(const char* vertexPath, const char* fragmentPath);
// use/activate the shader
void use();
// utility uniform functions
void setBool(const std::string &name, bool value) const;
void setInt(const std::string &name, int value) const;
void setFloat(const std::string &name, float value) const;
};
#endifReading from file
= 파일 -> string : filestream
Shader(const char* vertexPath, const char* fragmentPath)
{
// 1. retrieve the vertex/fragment source code from filePath
std::string vertexCode;
std::string fragmentCode;
std::ifstream vShaderFile;
std::ifstream fShaderFile;
// ensure ifstream objects can throw exceptions:
vShaderFile.exceptions (std::ifstream::failbit | std::ifstream::badbit);
fShaderFile.exceptions (std::ifstream::failbit | std::ifstream::badbit);
try
{
// open files
vShaderFile.open(vertexPath);
fShaderFile.open(fragmentPath);
std::stringstream vShaderStream, fShaderStream;
// read file's buffer contents into streams
vShaderStream << vShaderFile.rdbuf();
fShaderStream << fShaderFile.rdbuf();
// close file handlers
vShaderFile.close();
fShaderFile.close();
// convert stream into string
vertexCode = vShaderStream.str();
fragmentCode = fShaderStream.str();
}
catch(std::ifstream::failure e)
{
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::FILE_NOT_SUCCESFULLY_READ" << std::endl;
}
const char* vShaderCode = vertexCode.c_str();
const char* fShaderCode = fragmentCode.c_str();
[...]compile & link & error
// 2. compile shaders
unsigned int vertex, fragment;
int success;
char infoLog[512];
// vertex Shader
vertex = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
glShaderSource(vertex, 1, &vShaderCode, NULL);
glCompileShader(vertex);
// print compile errors if any
glGetShaderiv(vertex, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &success);
if(!success)
{
glGetShaderInfoLog(vertex, 512, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::VERTEX::COMPILATION_FAILED\n" << infoLog << std::endl;
};
// similiar for Fragment Shader
[...]
// shader Program
ID = glCreateProgram();
glAttachShader(ID, vertex);
glAttachShader(ID, fragment);
glLinkProgram(ID);
// print linking errors if any
glGetProgramiv(ID, GL_LINK_STATUS, &success);
if(!success)
{
glGetProgramInfoLog(ID, 512, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::PROGRAM::LINKING_FAILED\n" << infoLog << std::endl;
}
// delete the shaders as they're linked into our program now and no longer necessary
glDeleteShader(vertex);
glDeleteShader(fragment);void use()
{
glUseProgram(ID);
}void setBool(const std::string &name, bool value) const
{
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), (int)value);
}
void setInt(const std::string &name, int value) const
{
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), value);
}
void setFloat(const std::string &name, float value) const
{
glUniform1f(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), value);
}shader class 사용
Shader ourShader("path/to/shaders/shader.vs", "path/to/shaders/shader.fs");
[...]
while(...)
{
ourShader.use();
ourShader.setFloat("someUniform", 1.0f);
DrawStuff();
}= vertex/fragment shader 코드를 두개의 파일로 저장
= .vs .fs 확장자가 직관적
'그래픽스 > opengl' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [learn-OpenGL] Transformations (0) | 2021.07.26 |
|---|---|
| [learn-OpenGL] Textures (0) | 2021.07.25 |
| [learn-OpenGL] Triangle (0) | 2021.07.23 |
| [learn-OpenGL] Window 창 (0) | 2021.07.22 |
| [learn-OpenGL] Introduction : OpenGL (0) | 2021.07.22 |